The 2000 Ford Ranger stands as a testament to the ingenuity and engineering excellence found in the automotive world. This model, while over two decades old, continues to captivate enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike with its robust design and reliability. One aspect of maintaining such a vehicle is understanding its fuse box diagram, which is essential for troubleshooting electrical issues and ensuring safety. Delving into the intricacies of the fuse box helps illuminate both its functionality and the underlying connection to our behavior as users of these vehicles.
Understanding the fuse box is not merely a matter of replacing blown fuses; it serves as an interface between the driver and the intricate electrical system that powers everything from the headlights to the radio. In the 2000 Ford Ranger, the fuse box is strategically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side or occasionally in the engine compartment, making accessibility a key feature for owners looking to perform maintenance or repairs.
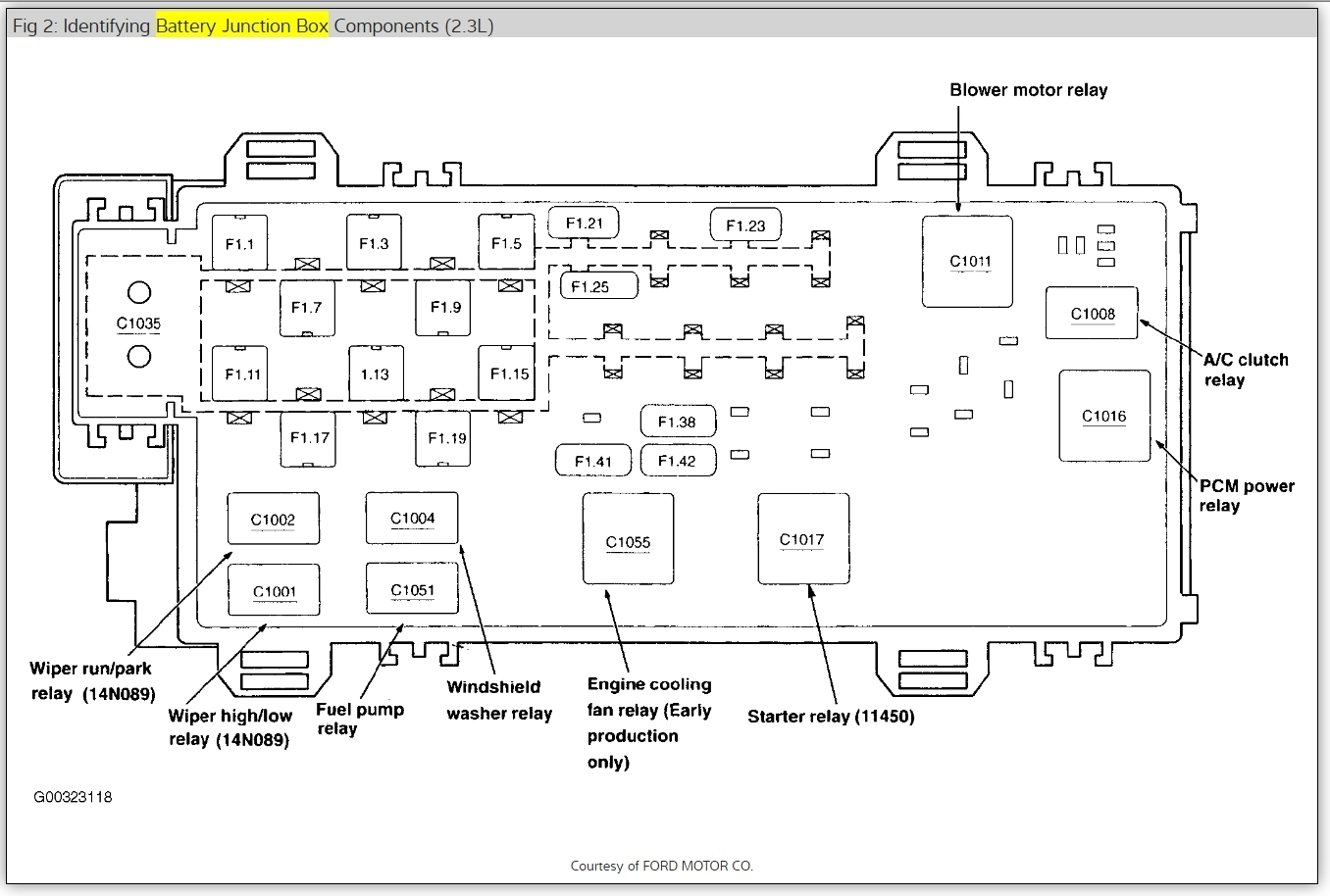
The fuse box in the 2000 Ford Ranger contains a myriad of fuses that regulate various electrical components. Each fuse is designed to protect its respective circuit by breaking the connection if an overload or short circuit occurs. This safety feature is paramount, as it prevents potential electrical fires or damage to components that could incur significant repair costs.
A complete understanding of the fuse box diagram is crucial for effective vehicle ownership. The diagram provides a compass-like tool, guiding the owner through the labyrinth of fuses. It illustrates the specific locations and functions of each fuse, often with indications for amperage, which indicates how much current the specific circuit can tolerate. For instance, if the vehicle’s interior lights become inoperative, consulting the fuse box diagram allows the owner to identify and replace the appropriate fuse with precision.
Each fuse slot is labeled, often corresponding with the specific function it controls: power windows, horn, wipers, and indicators. This systematic approach not only aids in diagnostics but also reflects a deeper observation into the nature of mechanical design; it showcases the interconnectedness of various components, a principle equally applicable in ecological systems. Just as a malfunction in one circuit can lead to the inefficacy of another, so too can disruptions in our environmental systems stem from a singular source of pollution or mismanagement.
The fascination with the 2000 Ford Ranger’s fuse box goes beyond mere practicality. It embodies a hands-on relationship with technology that many enthusiasts cherish, evoking a sentimental connection to the vehicles of their youth. This relationship fosters a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship involved in automobile manufacturing—a craft that faces unprecedented challenges today, particularly amid discussions surrounding sustainable practices in the automotive industry.
The production of vehicles carries significant environmental ramifications. The emissions produced during manufacturing, combined with the lifecycle of vehicles on the road, contribute to climate change. However, by actively engaging with the mechanics of our automobiles, including components like the fuse box, owners are empowered to extend the lifespan of their vehicles. This proactive approach alleviates the strain placed on manufacturing systems and reduces waste, echoing the principles of sustainable living.
Moreover, in an age marked by rapid technological advancements, the simplicity of older models such as the 2000 Ford Ranger can be refreshing. Understanding the inherent simplicity of its electrical systems allows for more comprehensive maintenance and fosters a culture of repair and reuse. In contrast to modern vehicles often laden with intricate computer systems and sensors, working on a Ranger emphasizes the importance of hands-on experience, stimulating a desire to preserve mechanical knowledge that may be lost in the digital age.
When tackling the myriad of electrical gremlins that may arise in a vehicle, it is essential to recognize the ecological implications of automotive repair. By choosing to repair rather than replace, one contributes to a larger movement advocating for sustainability in automotive practices. The principles of circular economy are exemplified in the repairable nature of vehicles like the Ford Ranger, promoting a future where automobiles are seen not just as consumable products, but as constructs capable of enduring multiple lifecycles.
Furthermore, the process of studying and engaging with the wiring and fuse systems within the Ford Ranger can serve as an educational platform in the broader context of climate awareness. Individuals who familiarize themselves with the inner workings of their vehicles can advocate for more environmentally conscious practices in their communities. This knowledge can ripple outward, promoting conversations around sustainable living, conservation, and the ethical implications of consumer choices.
In conclusion, the fuse box diagram of the 2000 Ford Ranger is more than just a functional guide; it is a gateway into understanding the vehicle’s electrical systems, as well as an avenue for meaningful engagement with sustainability issues. Beyond the realm of auto repair, it hints at deeper societal connections regarding resource use and ecological stewardship. As we confront the escalating challenges of climate change, embracing the fundamental aspects of vehicle maintenance can empower individuals to make informed choices—choices that resonate far beyond the dashboard, echoing through the very fabric of our environment.