In the realm of electrical engineering and technology, one cannot underestimate the significance of understanding the various units associated with the flow of electricity. Among these units, the frequency of alternating current (AC) is a pivotal concept that warrants in-depth exploration. This discourse unpacks the notion of frequency—specifically, how it is measured in hertz (Hz)—and delves into its implications across diverse applications.
What is Frequency?
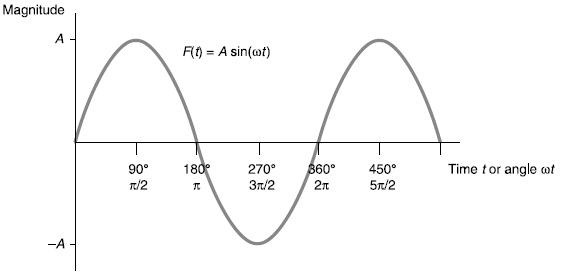
At its core, frequency refers to the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. In the context of electrical engineering, it frequently pertains to the oscillation of alternating currents. AC is characterized by the flow of electric charge that periodically reverses direction, as opposed to direct current (DC), where the electric charge flows in a singular direction. Thus, the frequency of AC reflects how many complete cycles of current oscillation transpire within a designated time frame, commonly quantified in hertz (Hz).
Understanding Hertz
The hertz, as a unit of frequency, is defined as one cycle per second. This is a straightforward yet pivotal explanation that quantitatively encapsulates the behavior of alternating currents. For example, a frequency of 60 Hz indicates that the AC supply completes 60 cycles in one second. This characteristic is especially crucial as it influences the behavior of electrical devices and systems, affecting performance and compatibility.
Historical Context
The term hertz pays homage to Heinrich Hertz, a German physicist who contributed significantly to the study of electromagnetism in the late 19th century. His experiments validated the existence of electromagnetic waves, setting the stage for technologies that form the backbone of modern electrical engineering. As such, using the hertz as a standard unit acknowledges this legacy while also providing an internationally recognized metric.
Types of AC Frequencies Around the World
Globally, the standard frequency for electrical power systems predominantly falls into two categories: 50 Hz and 60 Hz. Countries such as the United States, Canada, and several parts of Latin America utilize a frequency of 60 Hz. In contrast, much of Europe, Asia, and Australia predominantly operate at 50 Hz. This dichotomy has historical roots, reflecting divergent technological evolutions and preferences. The frequency choice can have profound implications, particularly for electronics and infrastructure.
The Impact of AC Frequency on Electrical Devices
Many electrical devices are meticulously engineered to operate at specific frequencies. For instance, electric motors, transformers, and other inductive components rely on the frequency of the alternating current for optimal functionality. Variations in frequency not only affect efficiency but can also lead to operational issues. Inadequate frequency might induce vibrations in motors, while excessive frequency can cause overheating and damage.
For example, a power supply designed for 60 Hz may perform inadequately or fail entirely if connected to a 50 Hz system. This mismatch underscores the importance of ensuring that devices match the operational frequency of the supply system to avoid malfunctions and ensure longevity.
Testing and Measurement
Accurate measurement of frequency is essential in both residential and industrial applications. Engineers and technicians utilize oscilloscopes, frequency counters, and other sophisticated tools to measure and analyze the frequency of AC signals. These instruments allow for real-time monitoring, ensuring that systems are operating within their designated parameters. Understanding the frequency of the AC can reveal vital information regarding the health and functionality of electrical systems.
AC Frequency and Its Role in Electronics
The frequency of alternating current plays a crucial role in the operation of electronic and electrical components. In signal processing, for instance, understanding frequency is imperative for the design of filters, amplifiers, and other integrated circuits. Components such as capacitors and inductors behave differently based on the frequency of the current passing through them. Consequently, frequency-selective circuits can effectively manipulate signals for various applications, from communications to audio technology.
The Frequency Spectrum: A Broader Perspective
While hertz predominantly measures the frequency of AC in traditional power systems, the concept of frequency extends far beyond. The frequency spectrum includes radio waves, sound waves, and light waves, each occupying its unique range of frequencies. In telecommunications, different frequencies, measured in kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), and gigahertz (GHz), are integral to broadcasting and data transmission. Thus, a comprehensive understanding of frequency spans a broad array of scientific and engineering disciplines.
Future Trends in Frequency Management
As technology continues to evolve, so does the management and utilization of alternating current frequency. The integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, invokes the necessity for advanced frequency control to synchronize power generation with load demands. Smart grid technologies and energy storage solutions are paving the way for more dynamic frequency regulation, enhancing the resilience and efficiency of modern electrical systems.
Conclusion
Understanding the frequency of alternating current measured in hertz provides an essential foundation for anyone engaged in the field of electricity and electronics. As we navigate through evolving technologies and try to harness renewable energy, the fundamental principles surrounding frequency remain central to ensuring that our electrical systems function effectively and sustainably. The complexities and nuances surrounding AC frequency elucidate a critical aspect of electrical engineering that continues to shape the modern world.