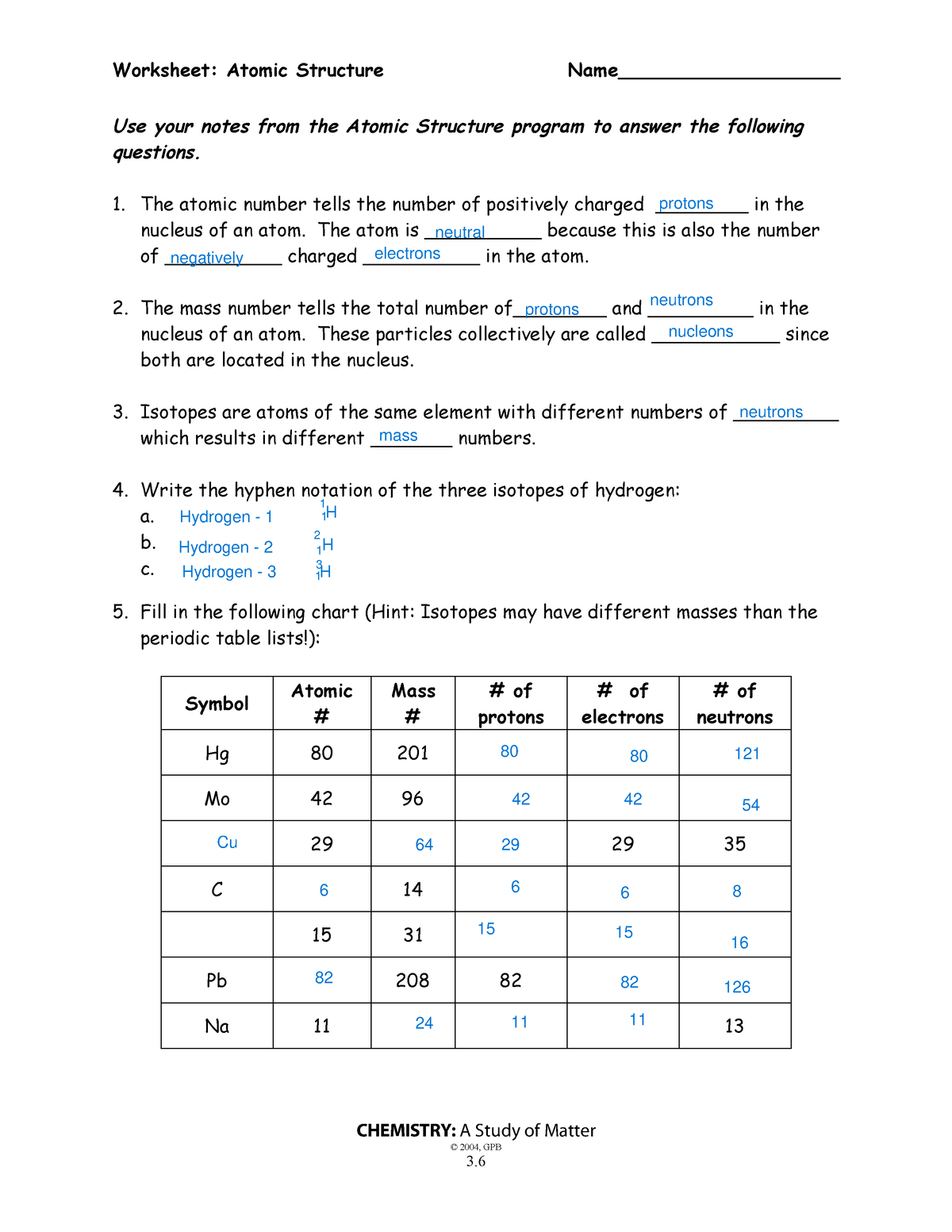
When it comes to the complexities of atomic structure, the nucleus often serves as a battleground of scientific curiosity. Have you ever pondered what exactly resides within this seemingly invisible realm? Imagine you’re a miniaturized scientist, equipped with a magnifying glass, peering into the very heart of matter. What do you think you would discover? Understanding the intricacies of the nucleus is crucial, not only in the field of chemistry but also in physics and biology. To demystify the nucleus and unravel its secrets, let’s dive deep into the essential components and functions that characterize this fundamental part of the atom.
First and foremost, let’s define what the nucleus is. Situated at the core of an atom, the nucleus is a dense region that contains protons and neutrons, collectively known as nucleons. Remember, the nucleus is not just a simple collection of particles; it plays a pivotal role in determining an atom’s identity and its properties. The number of protons in the nucleus, known as the atomic number, is what distinguishes one element from another. For instance, a carbon atom harbors six protons, while an oxygen atom contains eight. But what about the neutrons? These subatomic particles contribute to the mass of the atom but do not affect its elemental classification. It’s fascinating how such tiny entities can wield such immense influence, isn’t it?
Now, let’s compile a table detailing the fundamental characteristics of the nucleus. This exercise not only aids in comprehension but also serves as an excellent tool for retaining information. As you complete the following table, consider the significance of each item listed. How do these attributes correspond to the behavior of the atom as a whole?
| Component | Symbol | Charge | Mass (amu) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | p+ | +1 | 1 | Nucleus |
| Neutron | n | 0 | 1 | Nucleus |
As you fill in the information, you may notice that protons and neutrons have nearly identical masses, while electrons, which orbit the nucleus, are incredibly lighter in comparison. But why is it that the nucleus is so densely packed? The answer lies in the strong nuclear force—a fundamental interaction that binds protons and neutrons together, overcoming the repulsive electrical force between positively charged protons.
Now, let’s delve deeper into the characteristics of protons and neutrons, illuminating the role each plays in the overarching narrative of atomic structure. Protons, with their positive charge, do more than simply define an element’s identity; they also influence chemical behavior. The electronic structure of an atom is fundamentally determined by its proton count, guiding the formation of chemical bonds and reactions. Can you see how critical protons are in the realm of chemistry?
Neutrons, on the other hand, add another layer of complexity. They serve as stabilizers, especially in heavier elements where the repulsive forces among protons become increasingly significant. This brings us to isotopes—atoms of the same element that differ in neutron count. Imagine a world where carbon exists not just as carbon-12 (with six protons and six neutrons) but also as carbon-14, which has eight neutrons. This characteristic finds utility not just in nuclear physics but even in archaeology through carbon dating.
In addition to isotopes, the nucleus is also responsible for various forms of radioactive decay. This phenomenon occurs when an unstable nucleus loses energy through radiation, transforming into a different element or isotope. It raises an intriguing question: How does the structure of the nucleus influence its stability? The balance between protons and neutrons plays a crucial role in determining whether a nucleus is stable or prone to decay. Too many or too few neutrons compared to protons can lead to radioactivity, a topic that fascinates and terrifies in equal measure!
Let’s not overlook the role of the electron cloud, which, while not part of the nucleus itself, has a symbiotic relationship with it. Electrons occupy various energy levels outside the nucleus, creating a complex tapestry that dictates an atom’s reactivity and interactions with other atoms. The nucleus’s charge influences how many electrons will orbit and at what distances, generating the diverse range of chemical behaviors we observe in nature. Isn’t it extraordinary how this unseen force governs everything from the air we breathe to the stars we gaze at?
In conclusion, as you work through the atomic structure worksheet, remember that the nucleus is a marvel of creation made up of protons and neutrons, each playing a significant role in the grand science of atoms. Understanding its structure and behavior not only enriches our knowledge of the material world but also ignites the flames of curiosity and wonder. So, the next time you ponder the fundamental questions of existence, think of the nucleus and the incredible dynamics at play within the very building blocks of matter. Will you turn the page and continue your journey into the atom’s wondrous world?