Understanding the intricacies of mortgage payments can seem daunting, especially for first-time homebuyers. One particular figure that might strike interest is an $82,000 mortgage. Calculating the monthly payment on such a mortgage requires a blend of understanding interest rates, loan terms, and amortization techniques. This article endeavors to clarify how mortgage math works, providing you with an informative guide on what to expect and what factors to consider when determining your monthly mortgage payment.
At the core of mortgage calculations is the principal—the original sum borrowed. In this case, we begin with $82,000. However, there are additional layers to dissect. The interest rate, along with the duration of the loan, plays a critical role. Let’s explore these components in more detail.
1. The Crucial Role of Interest Rates
Interest rates can vary significantly based on your credit score, market conditions, and lender policies. For our calculations, let’s consider two common scenarios: a fixed interest rate of 4% and one at 6%. A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the life of the loan, providing stability against fluctuations in the market.
2. Loan Term: The Duration of Commitment
In conjunction with the interest rate, the term of the loan—commonly 15 or 30 years—greatly affects your monthly payments. A longer term typically results in lower monthly payments, but can lead to higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. Each scenario merits exploration:
- 30-Year Fixed Mortgage: Ideal for those looking for lower monthly payments. However, the interest accumulates over a longer period.
- 15-Year Fixed Mortgage: Higher monthly payments, yet significantly less interest is paid compared to a 30-year term.
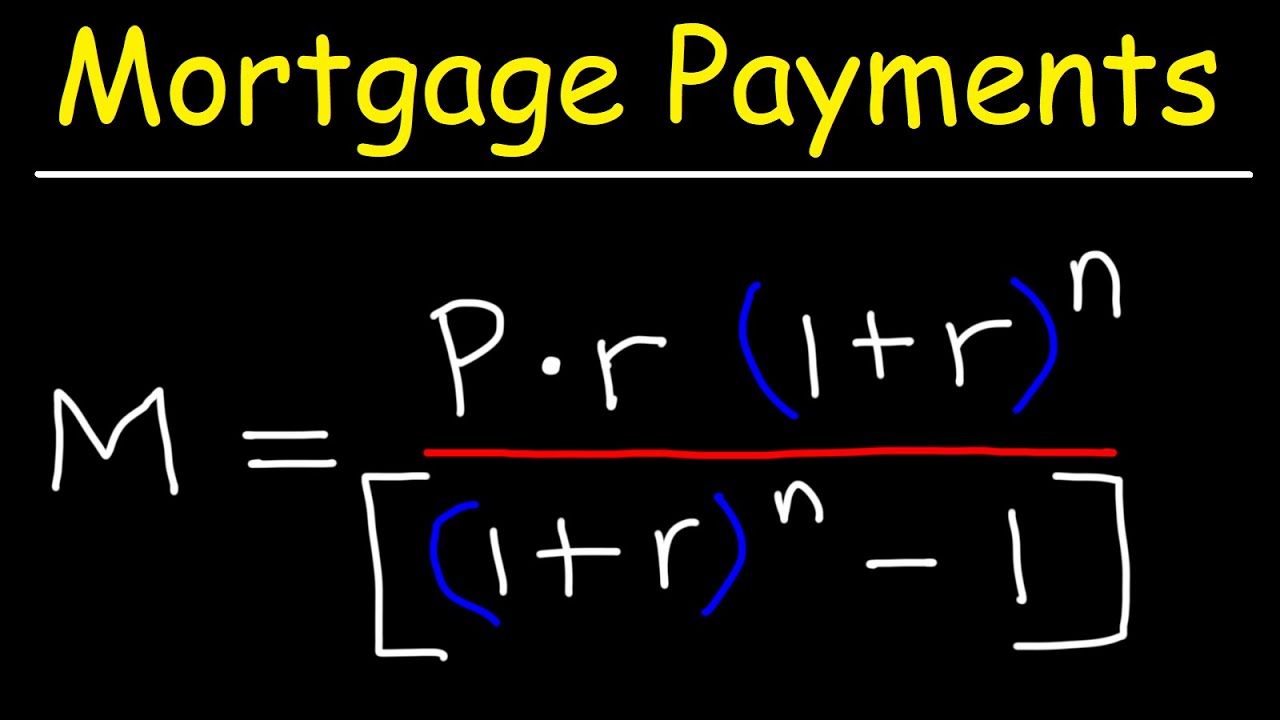
3. The Formula for Monthly Payments
Borrowers can employ the Monte Carlo simulation on mortgage calculators or utilize a straightforward formula:
M = P[r(1 + r)^n] / [(1 + r)^n – 1]Where:
- M = monthly payment
- P = principal amount ($82,000)
- r = monthly interest rate (annual rate divided by 12)
- n = number of payments (loan term in months)
Using this formula, we can calculate the monthly payments for both interest rates over a 30-year period.
4. Monthly Payment Scenarios
Now, let’s crunch the numbers:
Scenario 1: 4% Interest Rate (30 years)
Converting this into a monthly rate gives us:
0.04 / 12 = 0.00333333333The number of payments over a 30-year period would be:
30 * 12 = 360Inserting these figures into the formula yields:
M = 82000[0.00333333333(1 + 0.00333333333)^360] / [(1 + 0.00333333333)^360 – 1]The resulting monthly payment would be approximately:
$392.08Scenario 2: 6% Interest Rate (30 years)
Using the same formula at 6%, the monthly interest rate becomes:
0.06 / 12 = 0.005With the number of payments still being 360:
M = 82000[0.005(1 + 0.005)^360] / [(1 + 0.005)^360 – 1]This results in a monthly payment of approximately:
$494.985. Additional Costs
While the principal and interest determine the bulk of the payment, potential homeowners must also factor in additional costs that accompany most mortgages:
- Property Taxes: Typically assessed by local governments, these can vary widely.
- Homeowners Insurance: Provides protection against hazards and liabilities.
- Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): Required if your down payment is less than 20%.
Including these costs can inflate your monthly outlay significantly, affecting your overall budget.
6. Understanding the Amortization Process
Amortization is another significant aspect to consider. Each mortgage payment reduces the principal, and a portion goes toward interest. Early in the loan, more money goes to interest. As you progress, the balance shifts, allowing for little accumulation of equity early on.
7. Conclusion
In summary, understanding the mortgage math for an $82,000 loan is pivotal for informed financial decision-making. Through exploration of interest rates, loan terms, and ancillary costs, prospective homeowners can gain a clearer picture of their financial commitment. Remember to factor in the type of mortgage that aligns with your financial situation, as it could save you thousands over the lifetime of the loan. A well-informed borrower is better equipped to navigate the complexities of home financing, ensuring they make choices that lead to successful homeownership.