As the world grapples with the escalating consequences of climate change, a pivotal turning point lies within the realm of architectural practices. New building codes emerge not merely as regulatory instruments but as vital catalysts driving sustainable development. These enhanced standards are fundamentally reshaping how structures are designed, constructed, and operated, significantly mitigating their environmental footprints.
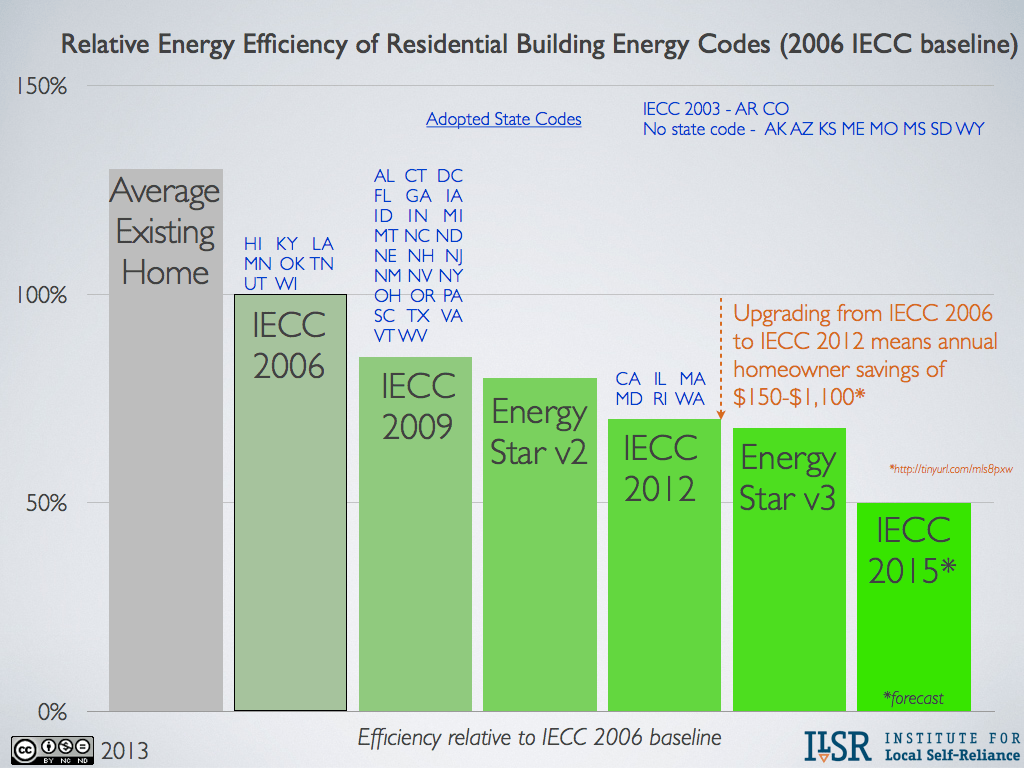
One of the foremost innovations in contemporary building codes is the emphasis on energy efficiency. Codes are now mandating stricter insulation requirements, optimized HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, and the integration of renewable energy resources such as solar panels. These stipulations ensure that new constructions consume less energy, thus reducing reliance on fossil fuels and curbing greenhouse gas emissions. The implementation of advanced technologies such as smart meters and automated lighting systems further enhances energy conservation, ensuring that buildings operate at peak efficiency.
In addition to energy efficiency, modern codes are increasingly addressing sustainability through material specifications. The adoption of eco-friendly materials—such as recycled steel or sustainably sourced timber—reduces the environmental toll associated with traditional building resources. This holistic approach not only minimizes waste but also promotes the longevity of structures, delivering economic benefits alongside environmental ones. Particularly noteworthy are codes that encourage the use of low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints and finishes, which dramatically improve indoor air quality, fostering healthier living environments.
Water conservation is another critical facet of contemporary building codes. By incorporating provisions for rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling systems, these regulations help mitigate water wastage. Moreover, the implementation of high-efficiency fixtures reduces overall water consumption. This is especially vital in regions facing drought or water scarcity, highlighting the codes’ role in resource stewardship.
Furthermore, the integration of resilience strategies into building codes addresses the urgent need to prepare for extreme weather events. Codes are increasingly requiring structures to withstand hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, thereby safeguarding both inhabitants and the environment. These forward-thinking measures not only protect investments but also contribute to community stability in the face of climate-related adversities.
Incorporating these diverse aspects, modern building codes signify a transformative approach to architecture and urban development. By fostering a synergy between ecological responsibility and innovative design, they not only contribute to environmental preservation but also inspire societal shifts towards sustainable living. Ultimately, the adoption and rigorous enforcement of these regulations represent a critical evolution in our collective endeavor to rescue the planet from the precipice of environmental degradation.