When it comes to pressure measurements, understanding conversions is essential for professionals across various industries, from engineering to meteorology. One common measurement unit is inches of mercury (inHg), which is often used in barometers and vacuum applications. In contrast, pounds per square inch (PSI) is a more widely recognized unit in many technical fields. Accurately converting between these two units can be crucial for ensuring appropriate pressure settings and readings.
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of pressure conversion, particularly focusing on how to convert inches of mercury to PSI. This conversion is not merely a mathematical exercise; it plays a pivotal role in practical applications such as calibrating instruments, understanding weather patterns, and even managing hydraulic systems.
To begin, it’s important to grasp the concept of pressure itself. Pressure arises from the force exerted by gas or liquid molecules colliding against a surface. This force, distributed over a given area, results in pressure measured in units such as PSI or inches of mercury. The relationship between these units can be articulated through a simple conversion factor. Specifically, 1 inch of mercury is equivalent to approximately 0.491 psi. Therefore, when you are tasked with converting inches of mercury to PSI, the formula is straightforward:
PSI = Inches of Mercury × 0.491
Let’s look at a practical example. Suppose you have a reading of 30 inches of mercury, typically associated with standard atmospheric pressure at sea level. To convert this to PSI, you would perform the following calculation:
30 inHg × 0.491 = 14.73 PSI
This calculation illustrates how atmospheric pressure, measured in inches of mercury, translates into pounds per square inch, allowing professionals to communicate and utilize pressure measurements accurately across different contexts.
One important aspect to consider when understanding pressure conversion is the context in which these measurements are applied. For meteorologists, atmospheric pressure readings in inches of mercury inform weather forecasting models. Higher readings often predict clear weather, while lower readings can indicate storms or inclement weather. For engineers and technicians working with pneumatic systems, precise PSI measurements directly affect system performance and safety.
Another relevant point is the concept of absolute pressure versus gauge pressure. Gauge pressure typically does not include atmospheric pressure, whereas absolute pressure does. When converting inches of mercury, it’s essential to be cognizant of whether your measurements are being taken as absolute or gauge pressure, as this distinction can influence your calculations. Gauge pressures can lead to discrepancies if assumed to equate to absolute values, thus affecting the outcome of your conversion.
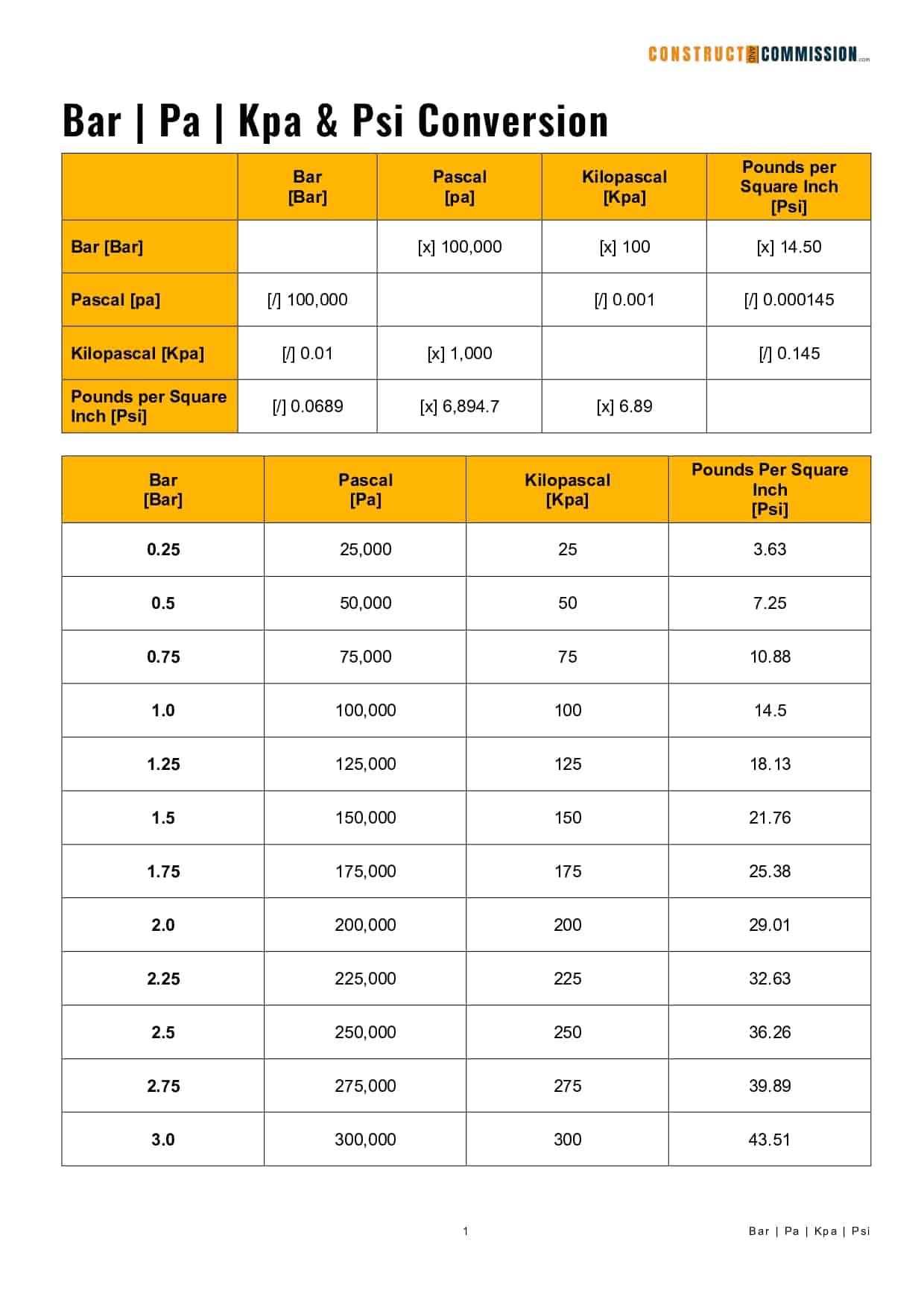
Moreover, pressure conversions extend beyond just inches of mercury and PSI. They encompass a spectrum of units commonly utilized across various fields, such as Pascals (Pa), kilopascals (kPa), and bar. This extends the relevance of understanding the basic conversion of inHg to PSI. Each unit has its own significance and preferred applications. Consider, for example, that 1 PSI is equal to 6,894.76 Pascals or about 0.0689476 bar. Being adept in converting between these units can simplify various engineering calculations and enhance clarity in communication across different disciplines.
For individuals engaged in specialized fields, the implications of pressure conversions can be profound. In the aerospace industry, for example, accurate atmospheric pressure readings are essential for flight dynamics and safety. Engineers designing high-altitude flight systems must account for changes in pressure as altitude increases, necessitating a firm grasp of these conversions. Similarly, in hydraulic engineering, the performance of systems is dictated by pressure measurements that must be carefully monitored and converted as necessary.
In practical scenarios, accessing a reliable pressure conversion calculator can be invaluable for professionals consistently working with various units. These tools streamline the process, allowing quick and accurate conversions without the need for manual calculation. However, knowing how to perform these conversions manually fosters a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts, which can be exceedingly beneficial in troubleshooting and practical applications.
As we navigate through pressure measurements and conversions, it’s crucial to acknowledge the broad implications of miscalculations. Whether in the field of HVAC systems, automotive engineering, or even off-grid plumbing designs, incorrect pressure readings can lead to inefficiencies, system failures, or even hazardous situations. As a result, a thorough comprehension of how to convert between inches of mercury and PSI is not merely an academic exercise but a practical necessity.
In closing, converting inches of mercury to PSI represents just a small piece of the intricate puzzle of pressure measurement and management. By understanding the relationship between various units, professionals can enhance their proficiency in their respective fields. This mastery enables more effective communication, better operational efficiency, and improved safety across diverse applications. Having the ability to effortlessly switch between units should be a fundamental component of any field that deals with pressure, providing a solid foundation for advanced studies and practical implementations.