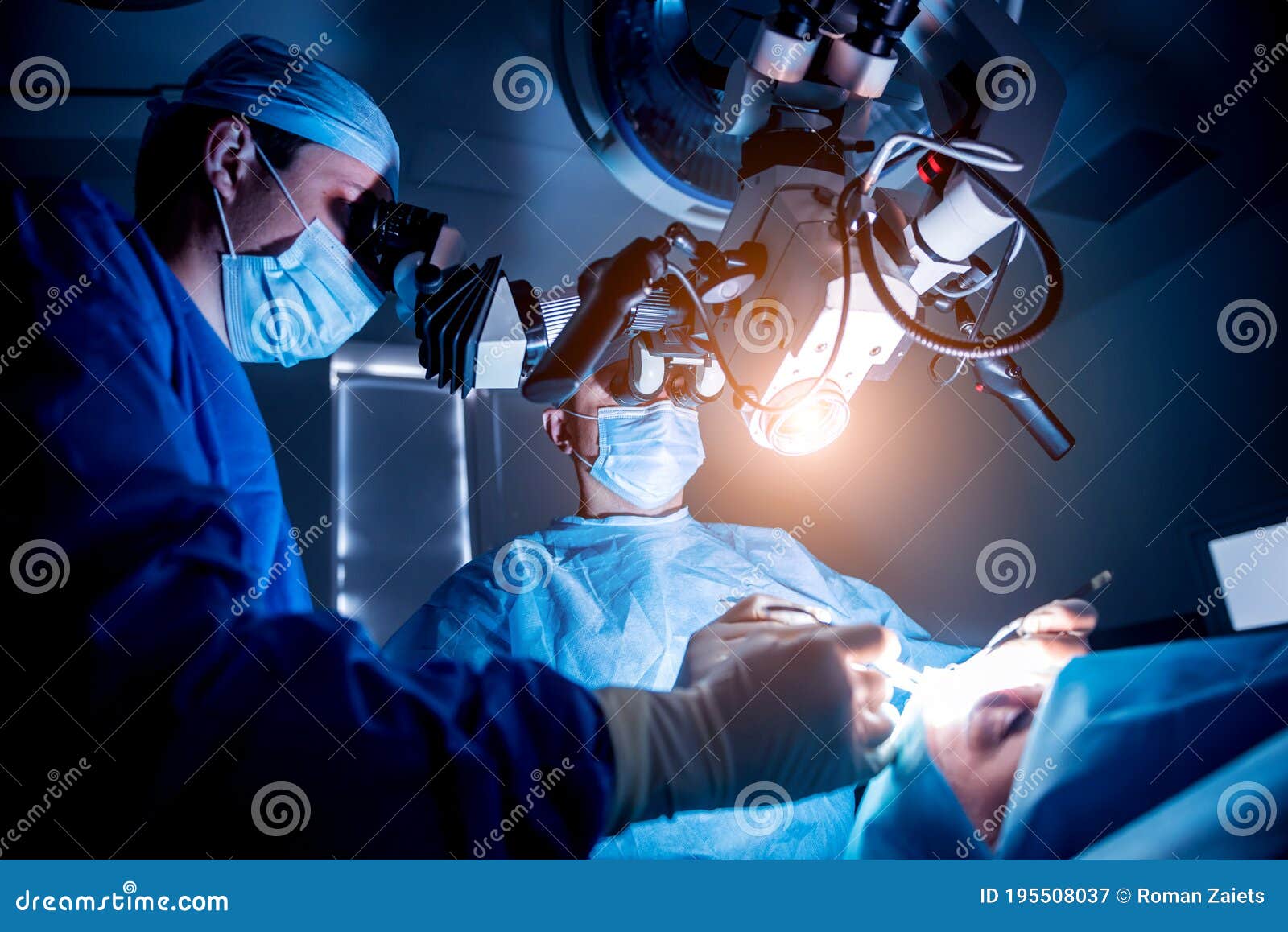
The realm of neurosurgery has undergone a profound transformation, particularly with the advent of robotic assistance in delicate procedures. Central to this evolution is the deployment of two armed surgical robots specifically designed to facilitate the removal of brain tumors. This innovative approach not only promises enhanced precision but also paves the way for a paradigm shift in how we perceive surgical interventions.
Traditionally, brain surgery has been fraught with challenges. The human brain, a complex and intricately woven network of neurons, requires meticulous care during any operation. Surgeons are often faced with confined operating spaces, where every movement must be calculated to avoid damaging critical structures. Enter the two-armed surgical robot, a groundbreaking device that significantly augments a surgeon’s capabilities. These highly sophisticated machines operate with unparalleled accuracy, allowing for movements at minute scales, reducing the risk of trauma to surrounding tissues.
The dual-arm configuration serves an essential purpose. One arm can be utilized for stabilization purposes, anchoring the surgical field, while the other executes the delicate maneuvers required for tumor excision. This coordination creates an environment where the operator can maintain focus on the intricacies of the task at hand, free from the usual constraints of fatigue or spatial limitations that often challenge human hands.
Moreover, these robots are equipped with advanced imaging technology, providing real-time visualization of the surgical field. This enhancement permits surgeons to navigate complex anatomy with remarkable dexterity. As a result, patients benefit from less invasive procedures, which correlate with quicker recovery times and diminished postoperative complications. The capacity for robots to perform these intricate tasks promotes a more favorable surgical experience, often sparking curiosity about the extent to which technology can be integrated into health care.
Beyond technical advantages, the introduction of robotic systems into neurosurgery raises essential ethical questions. It ignites a discussion around the role of technology in medicine—is it a complement to human skills or a potential replacement? While skeptics may voice concerns over reliance on automated systems, advocates argue that these robots serve as powerful assistants that enhance, rather than replace, the nuanced judgement and expertise of skilled surgeons. This discourse encourages a broader examination of how surgical practices might evolve as robotics mature.
In conclusion, the integration of two-armed surgical robots into brain tumor resections signifies not only a leap in technological advancement but also heralds an evolutionary step in surgical methodology. As curiosity around robotic surgery unfolds, it beckons further exploration into the future of surgical practices—an exploration that holds the potential for improved outcomes and frames an invigorating narrative for medicine in the 21st century.